Echo Chamber Effect on Emerging Social Media Platforms
Analysis of interaction patterns on platforms like Mastodon, BlueSky, and Truth Social
This project investigates the echo chamber effect across three emerging social media platforms in the “post-Twitter era”—Mastodon, BlueSky, and Truth Social. The study employs network science methods to examine the influence of ideological clustering and user interaction dynamics on opinion formation and polarization.
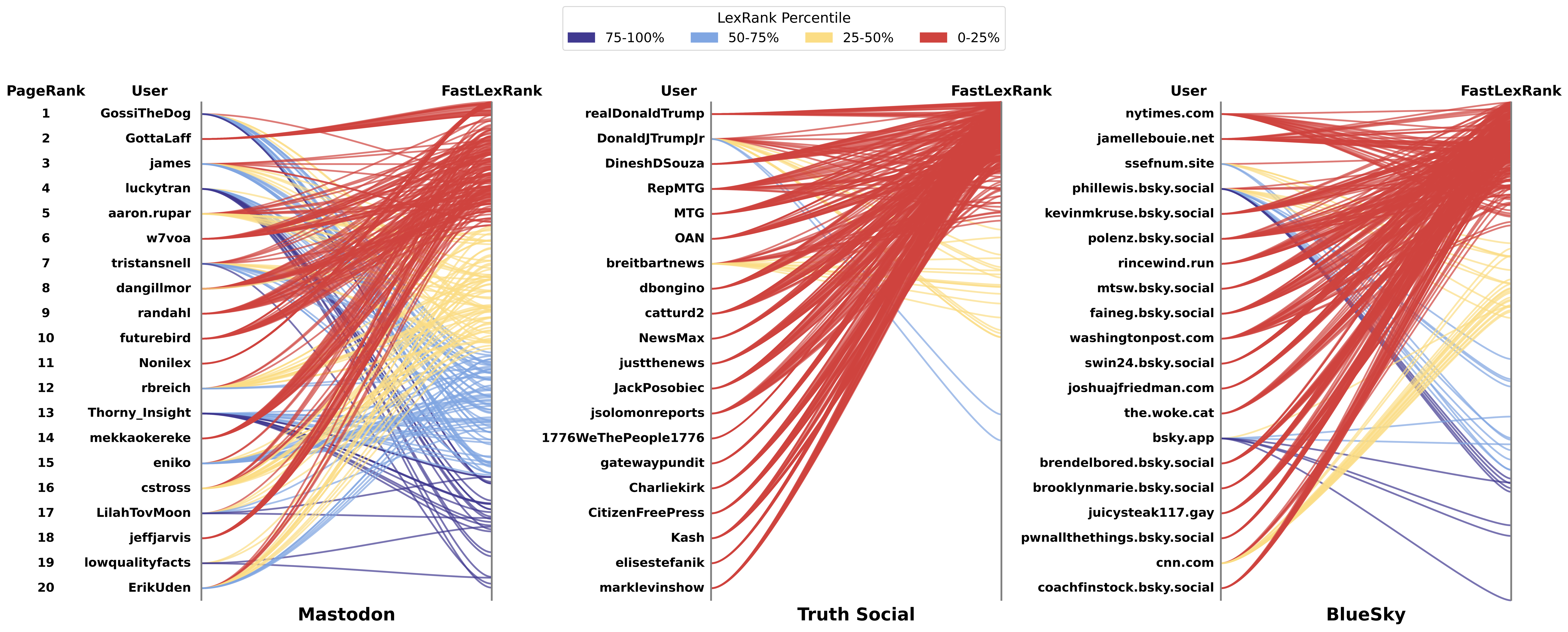
Graphs show influence mapping between users and their posts on BlueSky, Truth Social, and Mastodon.
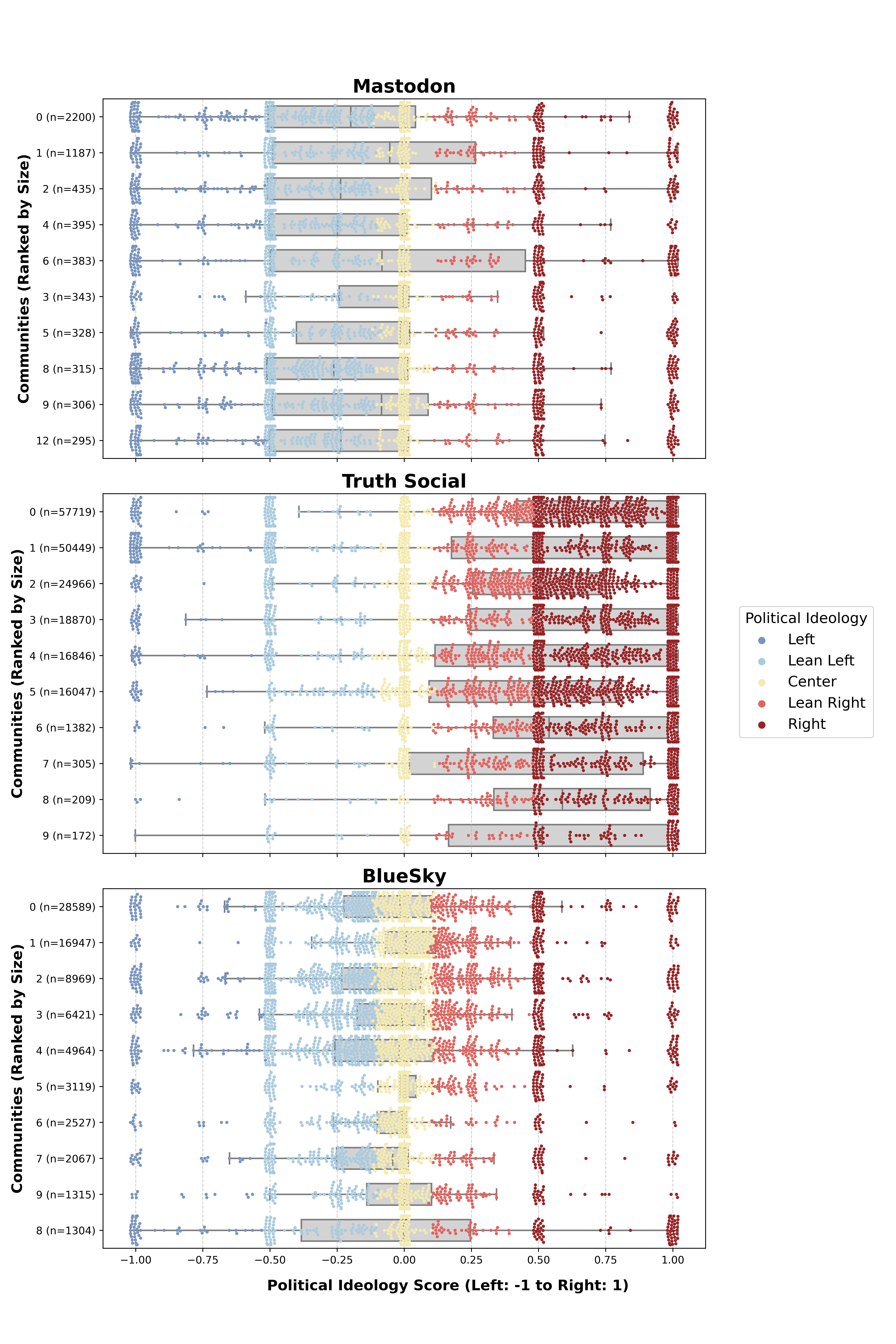
Graphs show composition of communities on BlueSky, Truth Social, and Mastodon.
Our methodology includes:
- Influence Mapping: Using PageRank and LexRank to identify users shaping discourse.
- Community Detection: Applying the Leiden algorithm to detect ideological clusters.
- Biased Random Walk Model: Simulating interactions to observe the likelihood of cross-ideological exposure.
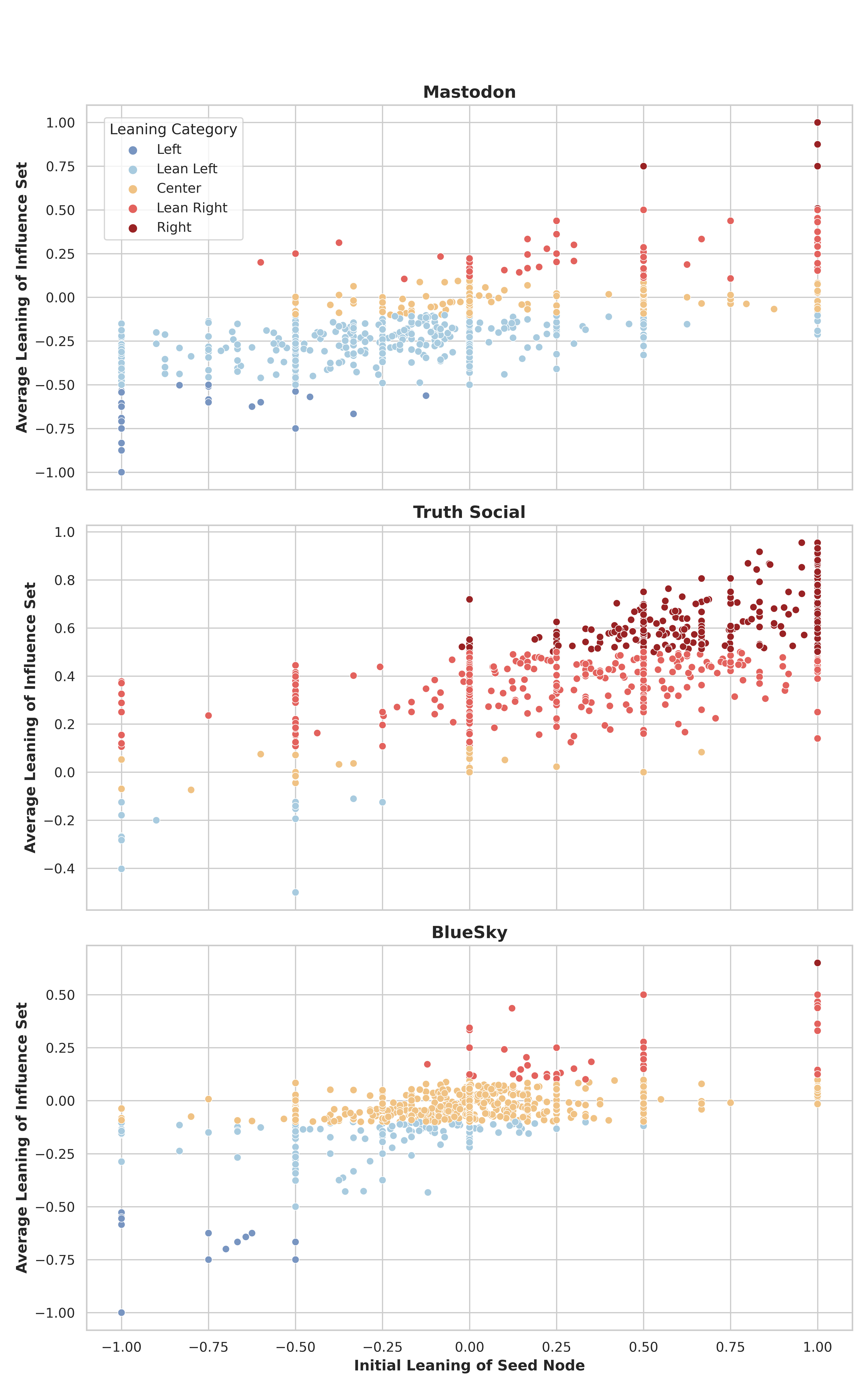
Simulations of biased random walks reveal strong echo chambers on Truth Social, while Mastodon displays more ideological diversity.
Key Findings
- Mastodon fosters cross-ideological exchanges, showing weaker echo chambers.
- BlueSky centers discussions around moderate views, reducing ideological polarization.
- Truth Social exhibits a strong echo chamber effect, aligning with its conservative audience and limited cross-ideological interaction.
This research highlights the role of platform architecture in shaping public discourse and the persistence of echo chambers in social media networks. You can read more in the full paper or access related publications.